According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 11,500 new cases of cervical cancer are diagnosed each year, and nearly 4,000 women die of this cancer annually. The CDC also notes that as many as 93 percent of cervical cancer cases could be prevented.
Integrative medicine specialist Dr. Dana Cohen has studied this topic in depth. A holistic MD, Dr. Cohen completed her medical training at St. George’s University (SGU) in 1995 and is now committed to helping patients incorporate holistic wellness practices into their daily routines to help reduce their risk level for this deadly disease.
Keep reading to learn her advice on how to prevent cervical cancer through healthy lifestyle changes.
Cervical cancer causes and risk factors
Before we cover the important preventative measures women can take to decrease their risk of cervical cancer, it’s helpful to learn about the causes and risk factors that contribute to the disease.
The prominent cause of cervical cancer is persistent infection with high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV). CDC data indicates that more than 42 million Americans are now impacted by this common sexually transmitted infection. While pervasive, most HPV infections clear up naturally without causing significant harm.
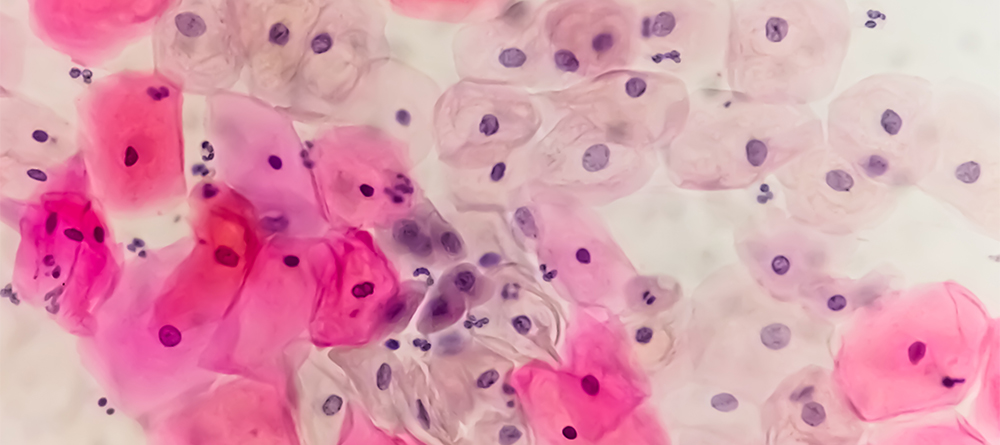
In some cases, however, the virus persists and can lead to changes in the host’s cervical cells. Cervical cancer begins when healthy cells in the cervix develop changes in their DNA, eventually forming a mass of cancerous cells called a tumor. These malignant cells can invade and destroy healthy body tissue. In time, they can even break away and spread to other parts of the body.
Even though HPV remains the primary cause of cervical cancer, there are other elements that can impact an individual’s susceptibility. Consider the following cervical cancer risk factors that reach beyond a high-risk HPV infection:
- Smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of cervical cancer; when individuals who smoke contract HPV, the infections tend to last longer and are less likely to go away.
- Increasing number of sexual partners: The greater number of sexual partners an individual maintains, the greater their chance becomes of getting HPV.
- Other sexually transmitted infections: Having other STIs such as herpes, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV/AIDS increases the risk of HPV.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals who are immunocompromised face a greater risk of developing cervical cancer if they contract HPV.
- Genetic factors: There are certain genetic predispositions that might aid in susceptibility; having a family history of cervical cancer does generally increase an individual’s risk level.
- Lack of screening: Failure to undergo regular cervical screenings can lead to undetected pre-cancerous changes.
- Poor socioeconomic conditions: Limited access to healthcare, including vaccinations and screenings, may contribute to higher risk levels overall.
When a patient receives a cervical cancer diagnosis, treatment options often begin with surgical intervention to remove the malignant cells. Other treatments may include medicines used to kill the cancer cells, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Cervical cancer prevention tips
The most prominent preventative measures against cervical cancer include getting vaccinated for HPV and adopting safe sexual practices to limit the risk of transmission. As the list of risk factors indicates, it can also help to quit smoking and have regular healthcare visits.
Additionally, Dr. Cohen notes that taking a proactive approach with integrative lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on cervical health outcomes. Consider these three holistic methods she teaches her patients so that they can support their immune systems to fight HPV and reduce their cervical cancer risk:

1. Nourish your immune system with functional nutrition
Dr. Cohen shares that a healthy immune system is the body’s best defense against high-risk infection. These three nutrients can help support immune health:
- Medicinal mushrooms: Adaptogenic mushrooms like chaga, shitake, and lion’s mane mushrooms contain bioactive compounds that can enhance immune function; they also have helpful anti-inflammatory properties.
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers (among other fruits and vegetables), vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that boosts the body’s immune response.
- Folate: Present in lentils, eggs, spinach, and bananas, folate is a B vitamin that is essential for DNA synthesis and cell division; low folate levels in women are associated with higher rates of developing cervical cancer from HPV.
2. Stay hydrated
Water’s role in supporting the immune system cannot be overstated, according to Dr. Cohen. Proper hydration helps maintain blood volume and circulation, which ensures that immune cells are able to travel efficiently through the body. White blood cells require a balanced internal environment to function optimally.
Remaining well-hydrated can also help reduce the burden placed on an individual’s immune system by working to remove toxins and waste products from the body. This enhances your immune response with more strength to focus on defending against infections.

3. Reduce Stress
Stress reduction can also have a significant impact in supporting immune function. Chronic stress has been found to weaken the immune system, making the body less effective in warding off infection.
Dr. Cohen regularly suggests a handful of holistic methods to help her patients reduce their stress levels:
- Practice mindfulness and meditation techniques to help promote relaxation and decrease anxiety.
- Commit to regular physical activity, which serves as a natural stress reducer by releasing endorphins.
- Try holistic therapies like aromatherapy, acupuncture, and massage to promote relaxation, balance energy, and relieve tension.
Learn to take charge of your health
Now that you know more about cervical cancer causes, risk factors, and prevention, it’s clear there are measures individuals can take to mitigate their susceptibility of developing this deadly disease.
As Dr. Cohen shares, incorporating proper nutrition, hydration, and stress reduction methods into your daily routine can strengthen your immune system and help reduce your risk of cervical cancer — particularly when combined with proper vaccination and safer sexual practices.
Practitioners like Dr. Cohen maintain that preventative medicine is key to helping individuals and communities stay a step ahead with their health and wellness. You can learn more in our article “What Is Preventative Medicine? A Look at What These Proactive Providers Do.”

